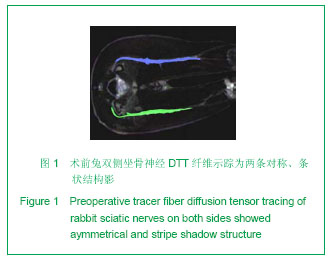
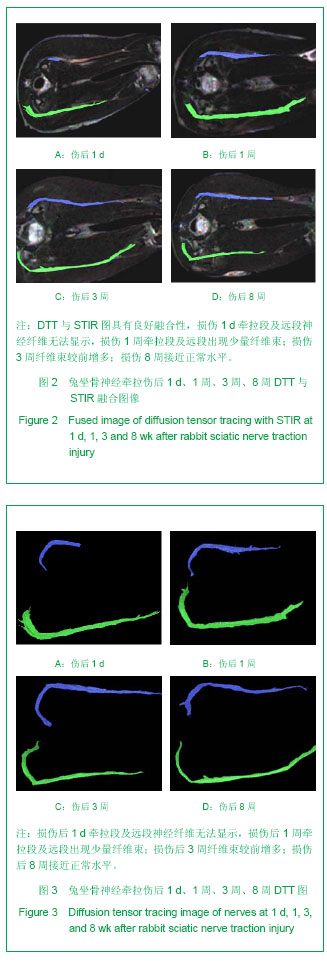
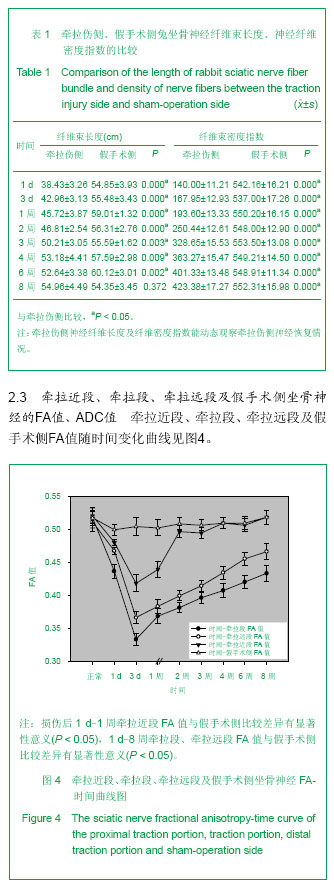
| [1] Meek MF, Stenekes MW, Hoogduin HM,et al. In vivo three-dimensional reconstruction of human median nerves by diffusion tensor imaging. Exp Neurol. 2006;198(2):479-482.
[2] Tagliafico A, Calabrese M, Puntoni M,et al. Brachial plexus MR imaging: accuracy and reproducibility of DTI-derived measurements and fibre tractography at 3.0-T.Eur Radiol. 2011;21(8):1764-1771.
[3] 李新春,陈健宇,刘庆余,等.正常臂丛节后神经MR神经成像术[J].中国医学影像技术,2004,20(1):105-107.
[4] Jambawalikar S, Baum J, Button T,et al. Diffusion tensor imaging of peripheral nerves. Skeletal Radiol. 2010;39(11): 1073-1079.
[5] 张帆,李坤成,于春水,等. 兔坐骨神经扩散张量纤维束示踪[J]. 放射学实践,2007,22(9):905-907.
[6] Hiltunen J, Suortti T, Arvela S,et al. Diffusion tensor imaging and tractography of distal peripheral nerves at 3 T. Clin Neurophysiol. 2005;116(10):2315-2323.
[7] 陈镜聪,李新春,孙翀鹏,等.正常成人近段坐骨神经的弥散张量成像[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2012,16(9):1647-1650.
[8] Tagliafico A, Calabrese M, Puntoni M,et al. Brachial plexus MR imaging: accuracy and reproducibility of DTI-derived measurements and fibre tractography at 3.0-T. Eur Radiol. 2011;21(8):1764-1771.
[9] Andreisek G, White LM, Kassner A,et al. Diffusion tensor imaging and fiber tractography of the median nerve at 1.5T: optimization of b value. Skeletal Radiol. 2009;38(1):51-59.
[10] van der Jagt PK, Dik P, Froeling M,et al. Architectural configuration and microstructural properties of the sacral plexus: a diffusion tensor MRI and fiber tractography study. Neuroimage. 2012;62(3):1792-1799.
[11] 孙翀鹏,许乙凯,陈妙玲,等. 1.5T MR兔坐骨神经弥散张量纤维束示踪b值优化[J]. 中国医学影像技术,2011,27(8):1528-1532.
[12] Lehmann HC, Zhang J, Mori S,et al. Diffusion tensor imaging to assess axonal regeneration in peripheral nerves. Exp Neurol. 2010;223(1):238-244.
[13] Takagi T, Nakamura M, Yamada M,et al. Visualization of peripheral nerve degeneration and regeneration: monitoring with diffusion tensor tractography. Neuroimage. 2009;44(3): 884-892.
[14] Wessig C, Koltzenburg M, Reiners K,et al. Muscle magnetic resonance imaging of denervation and reinnervation: correlation with electrophysiology and histology. Exp Neurol. 2004;185(2):254-261.
[15] 李新春,方学文,陈键宇,等.兔坐骨神经挤压伤的MRI与SEP对比研究[J].中国中西医结合影像学杂志,2007,5(3):178-180.
[16] Shen J, Duan XH, Cheng LN,et al. In vivo MR imaging tracking of transplanted mesenchymal stem cells in a rabbit model of acute peripheral nerve traction injury. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010;32(5):1076-1085.
[17] Duan XH, Cheng LN, Zhang F,et al. In vivo MRI monitoring nerve regeneration of acute peripheral nerve traction injury following mesenchymal stem cell transplantation. Eur J Radiol. 2012;81(9):2154-2160.
[18] 周翠屏,成丽娜,段小慧,等.兔坐骨神经急性牵拉伤模型的制作:MRI与病理对照[J].中国医学影像技术,2009,25(S1):5-7.
[19] Morisaki S, Kawai Y, Umeda M,et al. In vivo assessment of peripheral nerve regeneration by diffusion tensor imaging.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2011;33(3):535-542.
[20] Koeppen AH.Wallerian degeneration: history and clinical significance. J Neurol Sci. 2004;220(1-2):115-117. |